North American Deserts
The heart of the Southwest
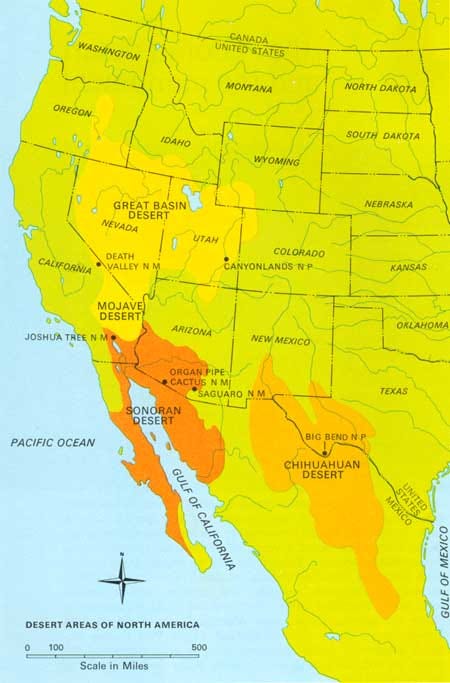
There are four main deserts in North America and they are mainly located between the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Madre Oriental mountain range in northeastern Mexico. They are Great Basin, Mojave, Sonoran and Chihuahuan Deserts.
A desert is sometimes defined as an area of land that receives less than 10 inches of precipitation a year. However, there’s a little more to it than that. In a desert, precipitation isn’t evenly distributed throughout the year. Weather patterns often create short, violent downpours that produce flash floods. Much of the water runs off before it can soak into the soil and a lot of moisture is lost to evaporation. The amount of evaporation in a desert often greatly exceeds the annual rainfall.
Close to one-third of the earth’s land surface is made up of both cold and hot deserts. Although some deserts are very hot, with daytime temperatures approaching 130°F, other deserts have cold winters or are cold year-round. Deserts are found on every continent and cover about one-fifth of Earth’s land area.
Three of the North American deserts -- the Chihuahuan, the Sonoran and the Mojave -- are classified as "hot deserts," because of their high temperatures during the long summer and the Great Basin Desert is a "cold desert".
The Great Basin Desert

The Great Basin Desert is a temperate desert with hot, dry summers and snowy winters and covers most of Nevada and parts of Utah, California, Oregon and Idaho. It is the only cold desert of the main four in North America and gets most of its precipitation from snow in the winter. It is in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada and Cascade Mountains. This desert is home to over 33 peaks whose summits are over 9,800 feet high, but its valleys have an elevation of over 3,900 feet. The annual precipitation in the eastern portions of the desert averages 12 inches while the west receives about 9 inches of rainfall.
The Great Basin is not a single basin, but hundreds of north-south mountain ranges divided by basins and valleys. The landscape is known scientifically as a “basin and range system.” It is particularly noted for its internal drainage system, in which precipitation falling on the surface leads to closed valleys and does not reach the sea.
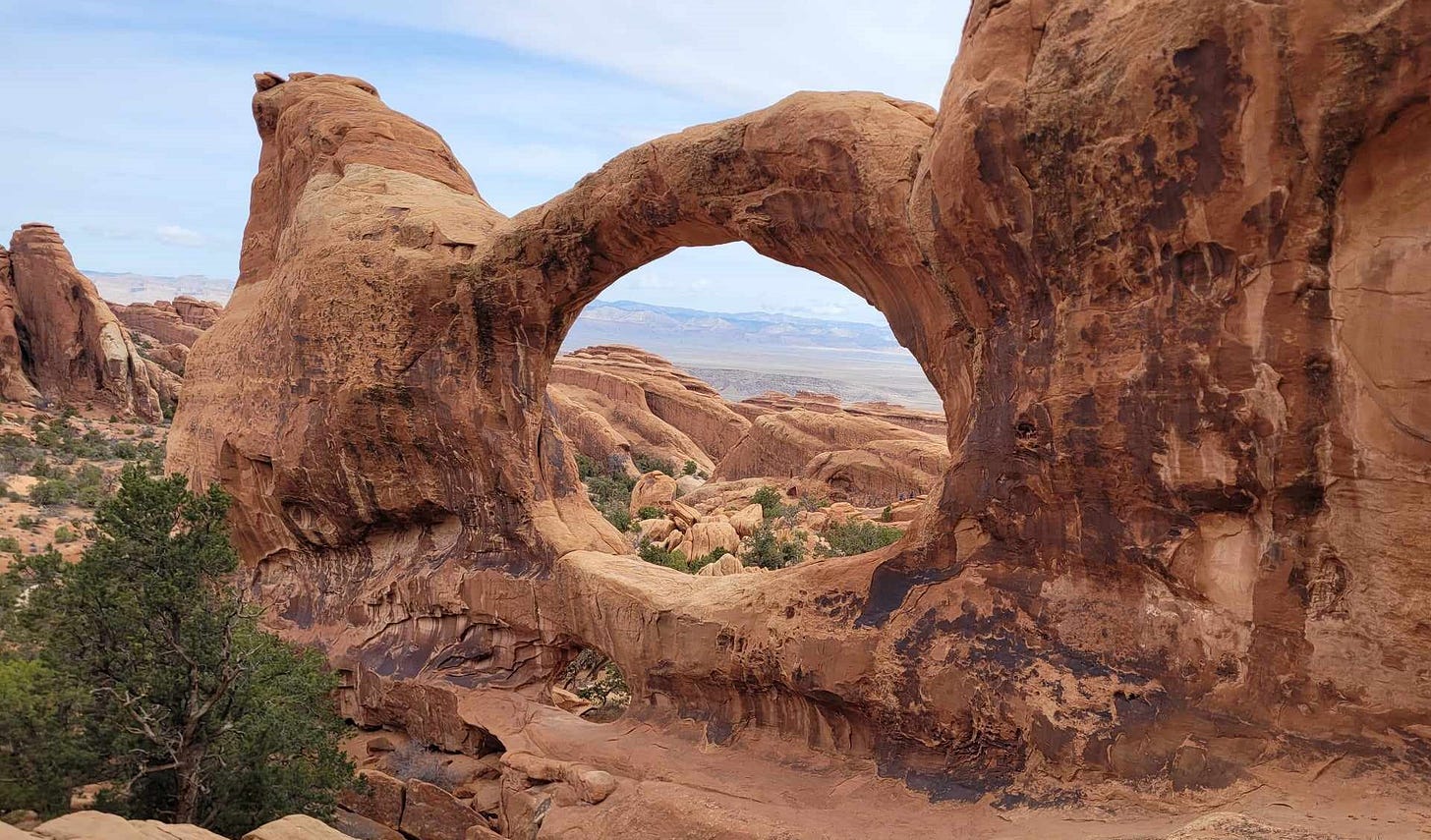
Great Basin National Park in Nevada, all five of the Utah National Parks, Monument Valley Tribal Park in Utah and Arizona, and the Painted Desert in Arizona lie in the Great Basin Desert.
The Sonoran Desert

The Sonoran Desert occupies the southern half of Arizona, southeastern California and most of the Mexican states of Sonora and Baja California. It grades into the Chihuahuan Desert to the east and the Mojave to the west. The Sonoran Desert is clearly distinct from nearby deserts because it provides subtropical warmth in winter and two seasons of rainfall. It receives frequent low-intensity winter (December/January) rains and violent summer (July/August) "monsoon" thunderstorms. Annual precipitation in the Sonoran Desert averages from 3 to 20 inches depending on the location.
The Sonoran Desert is thought to have the greatest species diversity of any desert in North America. It’s home to at least 60 species of mammals, more than 350 bird species, 20 amphibians, some 100 reptiles, and about 30 species of native fish. More than 2,000 species of plants have been identified and it’s the only place in the world where the Giant Saguaro (Carnegiea gigantea) grows in the wild.
Part of Joshua Tree National Park, California is located in the Sonoran Desert as is Saguaro National Park and Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument both in Arizona.
Mojave Desert
The Mojave is the smallest of the North American deserts and is the driest as it sits in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountain range. It is primarily situated in southern Nevada and southeastern California and a smaller part of the desert extends into Arizona and Utah. It merges with the Great Basin to the north and the Sonoran Desert to the south and southeast.
The desert has about 2,000 plant species including the Joshua Tree (Yucca brevifolia). The Joshua Tree is a great example of thriving desert plants as it has thicker leaves that can easily hold moisture.

The Mojave Desert is home to Death Valley (California and Nevada), one of the hottest places on earth in the summer. The western part of Joshua Tree National Park in California is part of the desert as well.
The Chihuahuan Desert
The Chihuahuan Desert is the largest desert in North America and covers southern New Mexico, eastern Arizona, portions of southwest Texas and extends south into Mexico’s Central Highlands. It is located in the rain-shadow of two mountain ranges: Sierra Madre Occidental to the west and the Sierra Madre Oriental to the east. This desert differs from the Sonoran and the Mojave deserts because it receives more summer rain during the monsoon thunderstorms and has colder winters. It receives almost all of its 6 to 20 inches of annual precipitation in the form of the monsoonal rain during the summer.
The 1,900-mile Rio Grande cuts through this desert which provides much-needed water to the area.
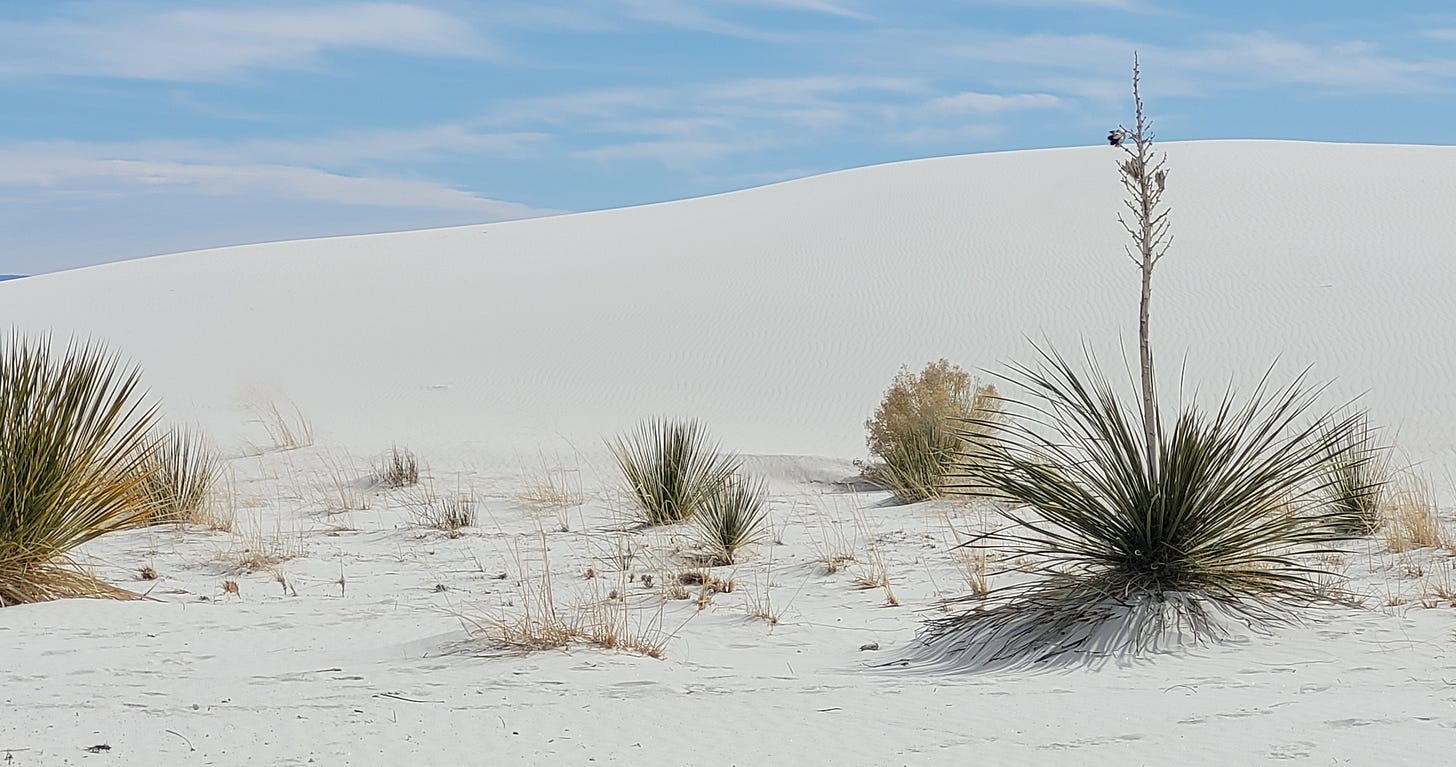
Big Bend National Park and Guadalupe Mountains National Park both in Texas and White Sands National Park are part of the Chihuahuan Desert.
Four Corners of the Southwest
The four North American Deserts are a big part of the Four Corners region. Ancient peoples called the deserts home and their descendants still live here today. Those of us transplanted here love the beauty and diversity of the area.
I call the Sonoran Desert my home and next time will be sharing some interesting facts about our “keystone” species the Giant Saguaro Cactus. It’s a common image of the American Southwest.